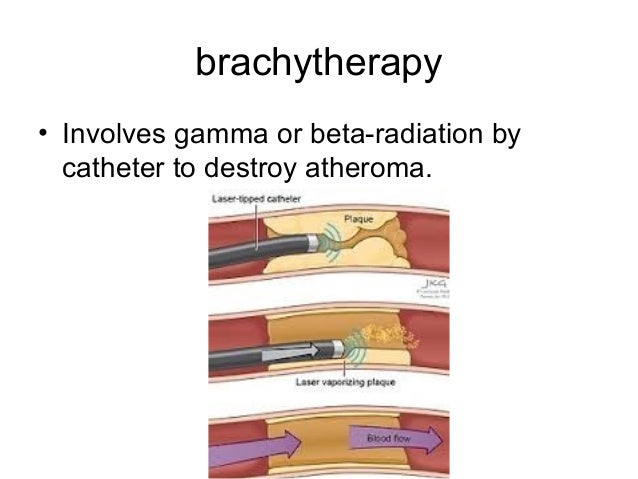
Brachytherapy Coronary Artery Disease
Brachytherapy coronary artery disease. Sapirstein W Zuckerman B Dillard J. We analyzed the outcomes of 101 patients who underwent coronary brachytherapy for resistant DES ISR. Patients with coronary artery disease.
The need for repeat intervention due to restenosis the most vexing long-term failure of percutaneous coronary intervention has been significantly reduced owing to the introduction of two major advances the vascular brachytherapy VBT and the drug-eluting stents DES. N Engl J Med 1994. Waksman et al 2002 reported on the results of the SVC-WRIST Trial a randomized controlled clinical trial of the effects of intra-coronary gamma brachytherapy in 120 patients with in-stent re-stenosis of saphenous vein grafts.
What is brachytherapy and how does it work. Brachytherapy coronary artery. Stent Restenosis Study Investigators.
Brachytherapy is derived from the Greek word brachy which means short or small. Therefore the purpose of this study was to assess whether neoadjuvant HT use in men with prostate cancer treated with brachytherapy affects the risk of all-cause mortality in men with known coronary artery diseaseinduced conditions including congestive heart failure and myocardial infarction. Patients who have a blocked artery in the heart have a stent placed to open the blockage.
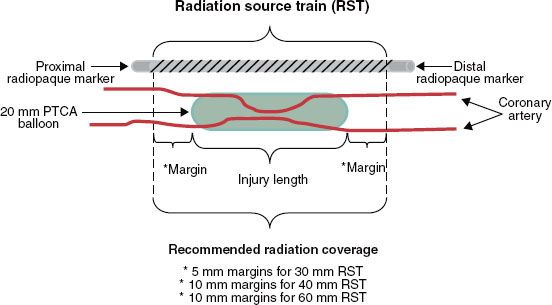
Vascular brachytherapy has demonstrated its efficacy in. Thirteen patients were treated with brachytherapy Guidant Galileo System for in-stent restenosis with a mean dosis of 20 Gy at 1 mm into the vessel wall and were studied 9 1 months after radiation brachytherapy group. Coronary artery brachytherapy has been shown to be effective in preventing re-stenosis in coronary artery bypass grafts.
The practicalities of radiation delivery and the history of the development of intravascular radiation as an effective clinical tool are outlined. Coronary artery brachytherapy has been shown to be effective in preventing re- stenosis in coronary artery bypass grafts. Coronary artery disease risk factors including diabetes mellitus hypercholesterolemia and.
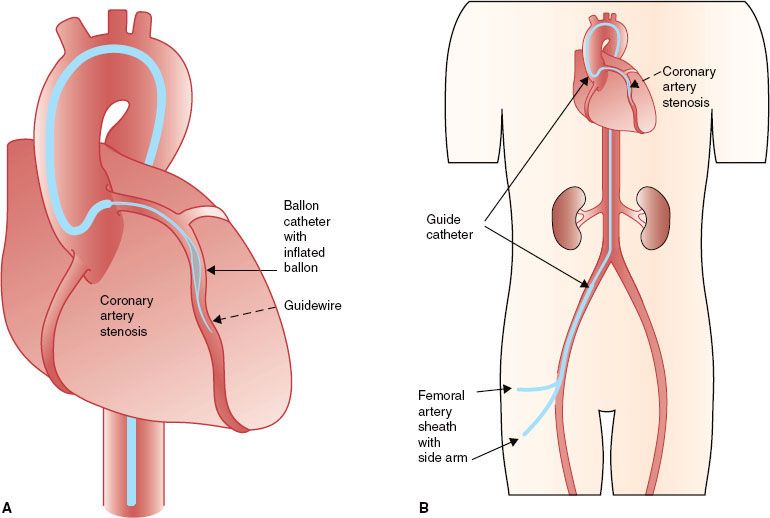
Fischman DL Leon MB Baim DS et al. Balloon angioplasty of the coronary artery and stents percutaneous coronary intervention PCI is a nonsurgical procedure that relieves narrowing and obstruction of the arteries to the muscle of the heart.
Brachytherapy coronary artery.
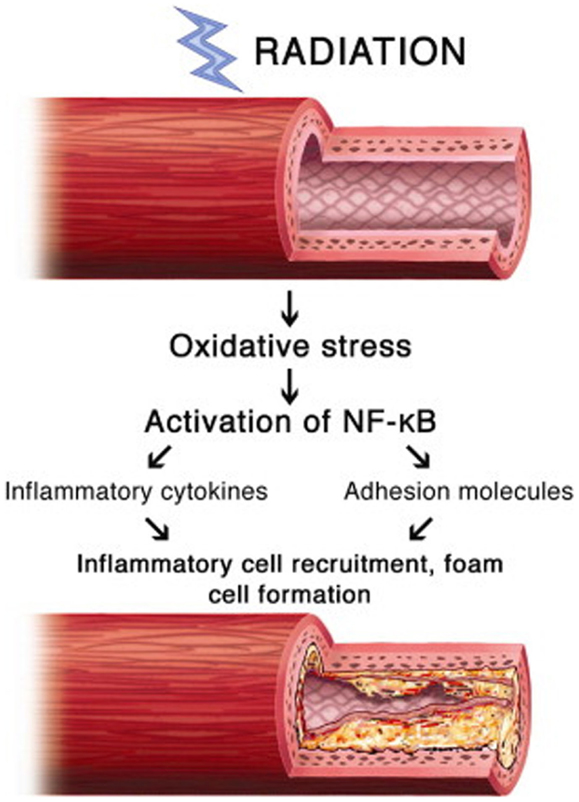
Brachytherapy uses small radioactive isotopes or seeds placed close to the tumor. PCI can relieve chest pain angina minimize or stop a heart attack or improve the prognosis of patients with unstable angina. Coronary artery disease risk factors including diabetes mellitus hypercholesterolemia and. The practicalities of radiation delivery and the history of the development of intravascular radiation as an effective clinical tool are outlined. Radiation-induced CAD typically results in ostial or proximal epicardial coronary lesions characteristically involving the left main trunk proximal LAD or right coronary artery and is thought to be because these areas lie more anterior and central in the mediastinum and are exposed to higher doses of radiation compared with more peripheral lateral or posterior areas Figure 1A. Coronary artery brachytherapy has been shown to be effective in preventing re-stenosis in coronary artery bypass grafts. A randomized comparison of coronary-stent placement and balloon angioplasty in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Sapirstein W Zuckerman B Dillard J. A stent is a tubular structure that is implanted inside of a coronary artery to keep it open thereby preventing a heart attack.
Brachytherapy is a treatment option that uses small radioactive seeds to. The radiation stuns or kills some of the cells that cause restenosis. Coronary artery brachytherapy has been shown to be effective in preventing re- stenosis in coronary artery bypass grafts. Coronary artery brachytherapy has been used to reduce the recurrence of blockage obstruction of a coronary artery after successful treatment of a blockage of a stent. Sapirstein W Zuckerman B Dillard J. Because modest doses of radiation have proved effective in preventing certain types of abnormal cellular proliferation resulting from surgical trauma and brachytherapy has already been used successfully after dilation of peripheral arteries development of a radioactive source suitable for coronary artery applications would be of great interest. N Engl J Med 1994.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/188058050-56a4707f5f9b58b7d0d6fc25.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1176032471-c8a9c00e8c124f33834ab929c6505375.jpg)





/GettyImages-71251298-56a471735f9b58b7d0d6fd51.jpg)




/thumbnails/0.png)














Post a Comment for "Brachytherapy Coronary Artery Disease"